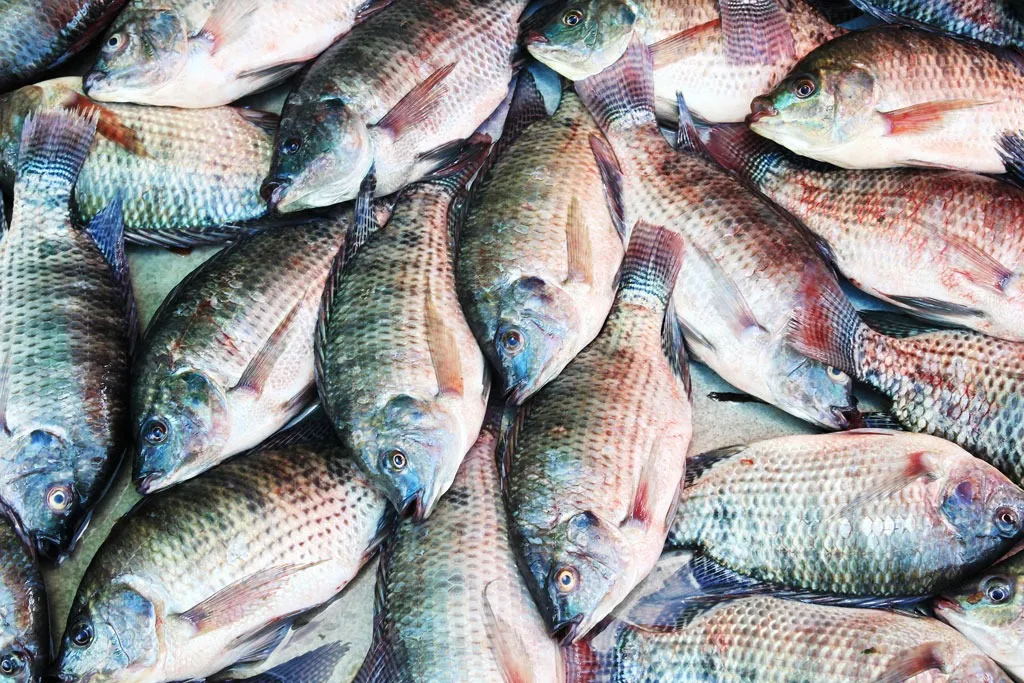
The Truth About Tilapia: Why It’s Not as Good as You Think
Tilapia once hailed as a healthy and sustainable choice, has come under scrutiny in recent years. While it’s often lauded for its affordability and mild taste, there’s growing concern about its nutritional value, environmental impact, and even potential health risks. In this article, we’ll delve into the various aspects of tilapia production, consumption, and its impact on health and the environment.
What is Tilapia?
Before we delve into why tilapia might not be the best choice, let’s first understand what exactly tilapia is. Tilapia is a type of freshwater fish that’s native to Africa, but it’s now farmed in many parts of the world, including the United States, China, and Latin America. It’s known for its mild flavor and versatility in cooking, which has contributed to its popularity in markets worldwide.
The Tilapia Industry: Environmental Concerns
One of the primary reasons why tilapia has garnered criticism is its environmental impact. The intensive farming practices used to rear tilapia often involve overcrowded ponds or cages, leading to pollution and the spread of disease. Additionally, the feed used in tilapia farming is often derived from wild fish stocks, contributing to overfishing and ecosystem disruption. You Can Also Read This Navigating USI Blackboard: A User-Friendly Guide
Nutritional Value: Is Tilapia Healthy?
Tilapia has long been promoted as a healthy choice due to its low fat and high protein content. However, recent studies have questioned its nutritional value. Unlike wild-caught fish, farmed tilapia may contain lower levels of omega-3 fatty acids and higher levels of omega-6 fatty acids, which can have inflammatory effects on the body when consumed in excess.
Health Risks Associated with Tilapia Consumption
Beyond its nutritional profile, there are concerns about potential health risks associated with tilapia consumption. Some studies have suggested that farmed tilapia may contain higher levels of contaminants such as pesticides, antibiotics, and heavy metals compared to other types of fish. These contaminants can pose risks to human health, particularly with long-term or high levels of consumption.
Alternatives to Tilapia: Making Better Choices
Given the environmental and health concerns surrounding tilapia, many consumers are seeking alternatives that are both sustainable and nutritious. Fortunately, there are plenty of options available, including other types of fish such as salmon, trout, and sardines, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and lower in contaminants. Plant-based protein sources like tofu, tempeh, and legumes are also excellent alternatives for those looking to reduce their consumption of animal products.
Conclusion
While tilapia may have once been considered a healthy and sustainable choice, it’s clear that there are significant concerns surrounding its production, consumption, and environmental impact. From pollution and overfishing to potential health risks for consumers, the drawbacks of tilapia outweigh its perceived benefits. As consumers, it’s essential to educate ourselves about the foods we eat and make informed choices that prioritize both our health and the health of the planet. By opting for alternatives to tilapia and supporting sustainable fishing practices, we can contribute to a healthier and more environmentally friendly food system for future generations.












Post Comment